
FREE EASY KETO DINNERS EBOOK
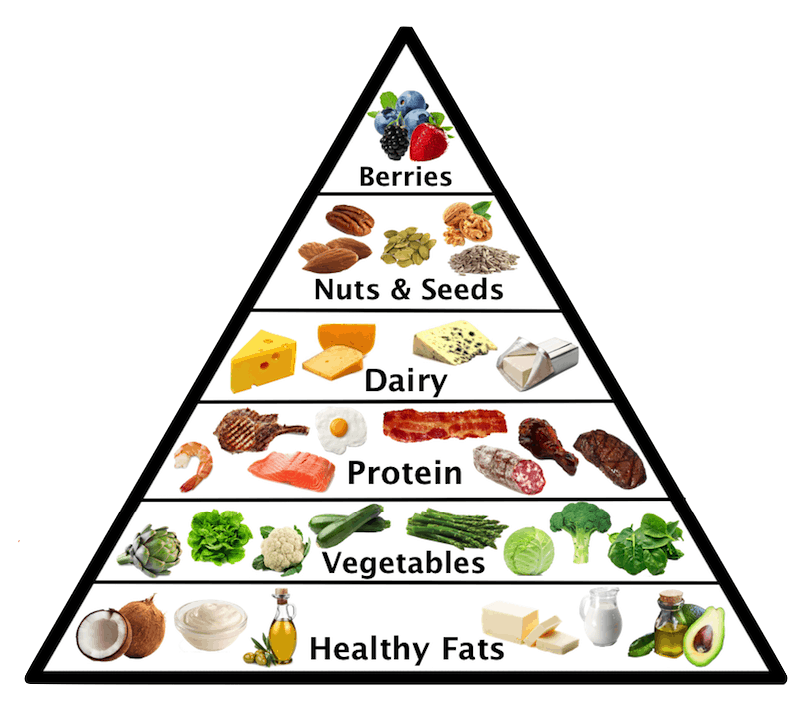
The Ketogenic is a high fat, low carb and moderate protein diet that depends on the bodily state of ketosis. In the standard biological process sugar or carbohydrates are stored as fat in order to be used as energy later. When you’re consistently eating food rich in carbohydrates, your body produces glucose for energy and this serves as the go-to source for powering your body’s processes.
Since the glucose is being used as a primary energy, your fats are not needed and are therefore stored. Typically on a normal, higher carbohydrate diet, the body will use glucose as the main form of energy. By lowering the intake of carbs, the body is induced into a state known as ketosis.
Ketosis is a natural process the body initiates to help us survive when food intake is low. During this state, we produce ketones, which are produced from the breakdown of fats in the liver. On a ketogenic diet, your entire body switches its fuel supply to run almost entirely on fat. Insulin levels become very low, and fat burning increases dramatically.
The end goal of a properly maintained keto diet is to force your body into this metabolic state. We don’t do this through starvation of calories but starvation of carbohydrates, typically under 20-50 grams a day.
While some people find ketogenic diets to be quite a change from what they are accustomed to eating, it needs to be realized that it also has many other benefits, such as less hunger and a steady supply of energy, keeping you alert and focused.
Many people find that it is beneficial in losing weight rather quickly. Part of this reason is because when your body starts converting fat into energy, that you will lose your cravings for sugar.
Different Types of Ketogenic Diets
There are several versions of the ketogenic diet, including:
- Standard ketogenic diet (SKD): This is a very low-carb, moderate-protein and high-fat diet. It typically contains 75% fat, 20% protein and only 5% carbs.
- Cyclical ketogenic diet (CKD): This diet involves periods of higher-carb refeeds, such as 5 ketogenic days followed by 2 high-carb days.
- Targeted ketogenic diet (TKD): This diet allows you to add carbs around workouts.
- High-protein ketogenic diet: This is similar to a standard ketogenic diet, but includes more protein. The ratio is often 60% fat, 35% protein and 5% carbs.
How to Know if You're in Ketosis
You can measure if you’re in ketosis via urine using Ketone Strips
Here are some physical signs that you are on the right path:
- Increased Urination: Keto is a natural diuretic, so you have to go to the bathroom more. Acetoacetate, a ketone body, is also excreted in urination and can lead to increased bathroom visits for beginners.
- Dry Mouth: The increased urination leads to dry mouth and increased thirst. Make sure that you’re drinking plenty of water and replenishing your electrolytes (salt, potassium, magnesium).
- Bad Breath: Also known as “Keto Breath”. Acetone is a ketone body that partially excretes in our breath. It can smell sharp like over ripe fruit, similar to nail polish remover. It’s usually temporary and goes away long term.
- Reduced Hunger & Increased Energy: Usually, after you get past the “keto flu,” you’ll experience a much lower hunger level and a “clear” or energized mental state.

